Categories:
Base Metals
/
General Market Commentary
Topics:
General Base Metals
/
General Market Commentary
What a difference a year makes: gloom and doom at Metals Week
The metals world is descending on London for the biggest annual bash in the industry’s calendar, but there’s not much to celebrate.
At last year’s LME Week, the industry was mostly optimistic. This time, things are looking bleak.
The outlook for some key metals is at the weakest since the financial crisis as the U.S.-China trade war and a synchronized global slowdown pummel consumption and investor sentiment. Economic bellwether copper is flashing warning signals, with demand growth stalling this year as manufacturing contracts.
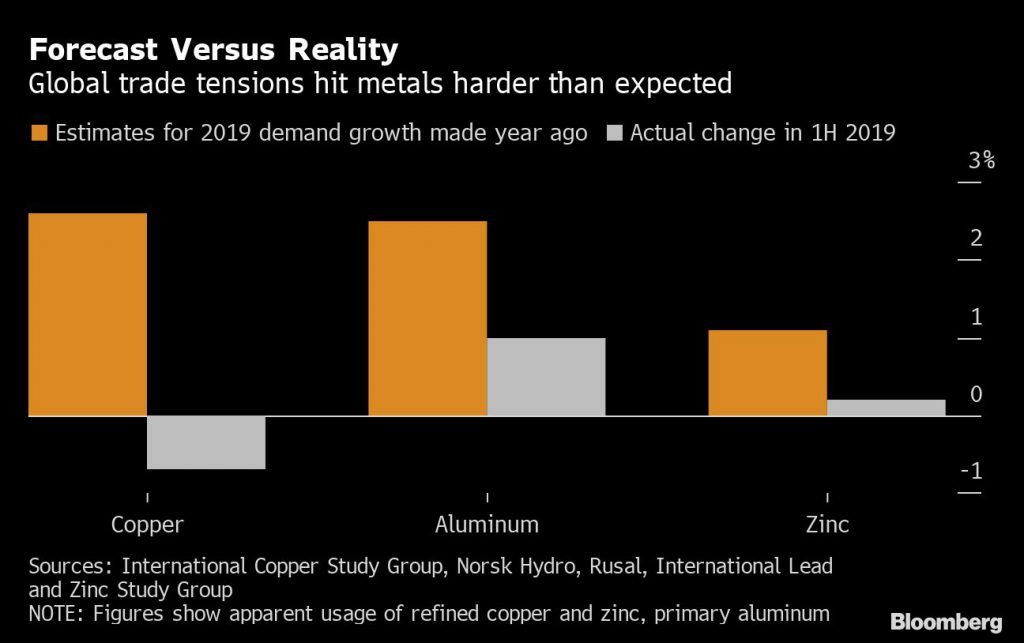
The only standout in the group is nickel, which has surged amid concerns about tight supply.
For more, listen to this mini-podcast on the weakness in metal markets
Overall, though, there’s “a no-growth picture for the commodity markets for the foreseeable future,” said Mark Hansen, chief executive officer of metals trader Concord Resources Ltd. The trade war “has dragged on now so long that it is impacting people’s willingness to make investments and have confidence in the foreseeable future.”
Here are five charts that show how things have turned bleak for most metals, with nickel as the clear exception:
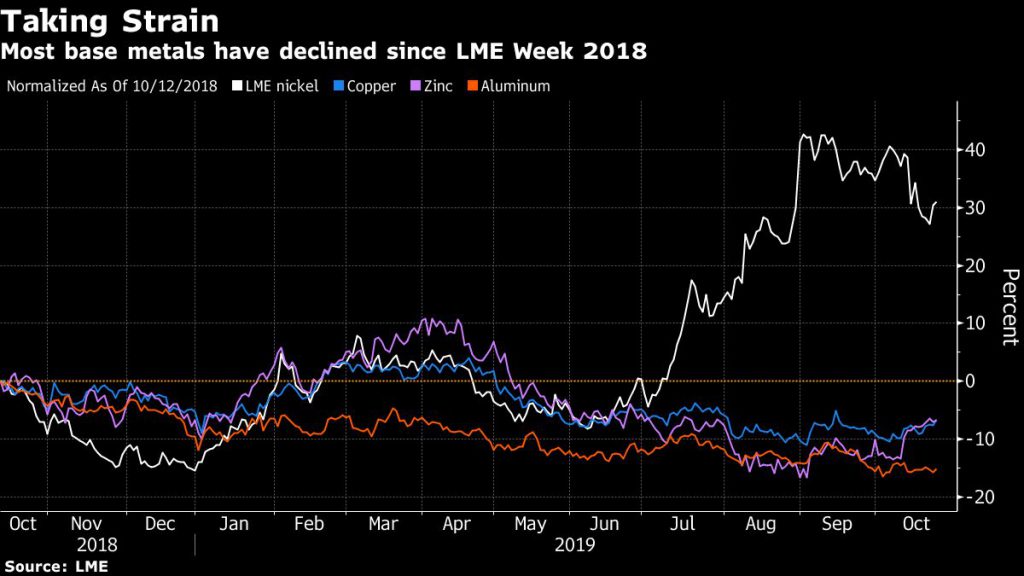
1. PMI pain
Copper is especially vulnerable to a global manufacturing slowdown because it’s used in such a wide range of products and industries, from plumbing to power cables and car radiators to high-tech electronics.
The International Copper Study Group expects the market will swing into a surplus next year as new capacity is added in China and some smelters and refineries ramp up after operational setbacks.
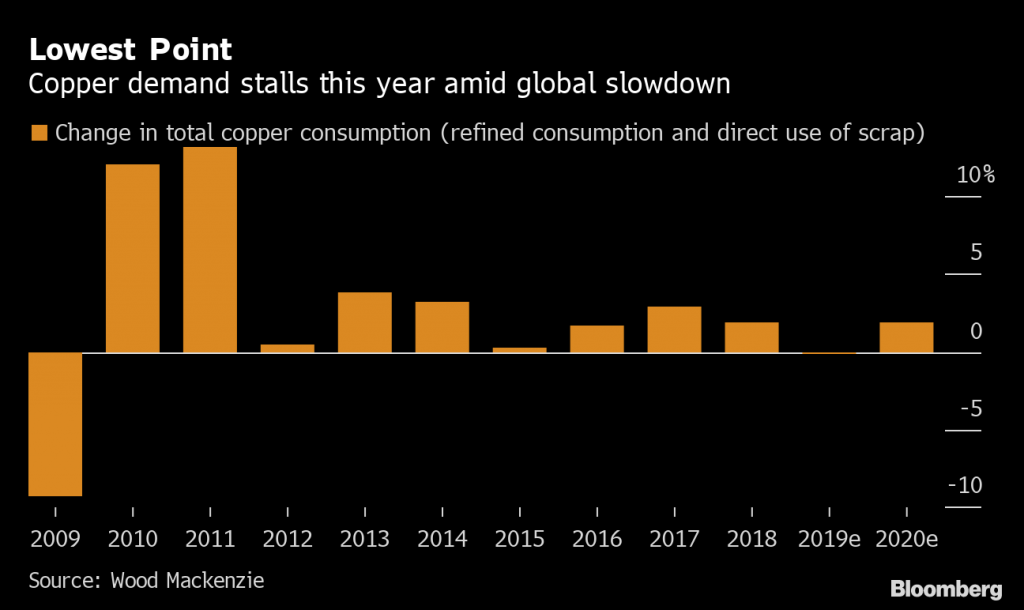
2. Demand stalls
Global copper demand — total consumption of refined metal and direct use of scrap — will probably decline 0.2% this year, due to a contraction in Europe and a slowdown in the U.S., according to Wood Mackenzie.
“Given the size of the market, it’s essentially flat year-on-year,” said Wood Mackenzie analyst Eleni Joannides. “But that means that the growth is at its weakest since the global financial crisis.”
To be sure, the supply outlook has tightened this month as civil unrest in top supplier Chile disrupted some mines and halted others. More widely, limited new mine supply is among the factors helping support copper prices despite the gloomy demand outlook — futures on the London Metal Exchange have fallen less than 1% this year.